Air Conditioner
Background
Residential and commercial space-cooling demands are increasing steadily throughout the world as what once was considered a luxury is now seemingly a necessity. Air-conditioning manufacturers have played a big part in making units more affordable by increasing their efficiency and improving components and technology. The competitiveness of the industry has increased with demand, and there are many companies providing air conditioning units and systems.
Air conditioning systems vary considerably in size and derive their energy from many different sources. Popularity of residential air conditioners has increased dramatically with the advent of central air, a strategy that utilizes the ducting in a home for both heating and cooling. Commercial air conditioners, almost mandatory in new construction, have changed a lot in the past few years as energy costs rise and power sources change and improve. The use of natural gas-powered industrial chillers has grown considerably, and they are used for commercial air conditioning in many applications.
Raw Materials
Air conditioners are made of different types of metal. Frequently, plastic and other nontraditional materials are used to reduce weight and cost. Copper or aluminum tubing, critical ingredients in many air conditioner components, provide superior thermal properties and a positive influence on system efficiency. Various components in an air conditioner will differ with the application, but usually they are comprised of stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant metals.
Self-contained units that house the refrigeration system will usually be encased in sheet metal that is protected from environmental conditions by a paint or powder coating.
The working fluid, the fluid that circulates through the air-conditioning system, is typically a liquid with strong thermodynamic characteristics like freon, hydrocarbons, ammonia, or water.
Design
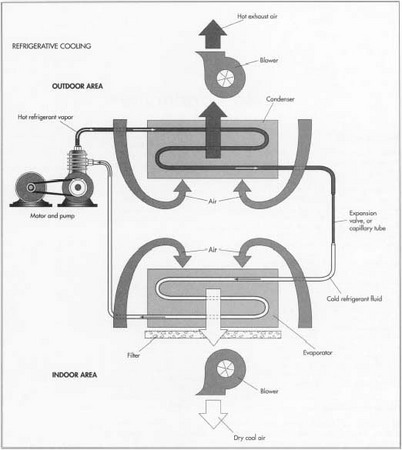
All air conditioners have four basic components: a pump, an evaporator, a condenser, and an expansion valve. All have a working fluid and an opposing fluid medium as well.
Two air conditioners may look entirely dissimilar in both size, shape, and configuration, yet both function in basically the same way. This is due to the wide variety of applications and energy sources available. Most air conditioners derive their power from an electrically-driven motor and pump combination to circulate the refrigerant fluid. Some natural gas-driven chillers couple the pump with a gas engine in order to give off significantly more torque.
As the working fluid or refrigerant circulates through the air-conditioning system at high pressure via the pump, it will enter an evaporator where it changes into a gas state, taking heat from the opposing fluid medium and operating just like a heat exchanger. The working fluid then moves to the condenser, where it gives off heat to the atmosphere by condensing back into a liquid. After passing through an expansion valve, the working fluid returns to a low pressure
The Manufacturing
Process
Creating encasement parts from galvanized sheet metal and structural steel
- 1 Most air conditioners start out as raw material, in the form of structural steel shapes and sheet steel. As the sheet metal is processed into fabrication cells or work cells, it is cut, formed, punched, drilled, sheared, and/or bent into a useful shape or form. The encasements or wrappers, the metal that envelopes most outdoor residential units, is made of galvanized sheet metal that uses a zinc coating to provide protection against corrosion. Galvanized sheet metal is also used to form the bottom pan, face plates, and various support brackets throughout an air conditioner. This sheet metal is sheared on a shear press in a fabrication cell soon after arriving from storage or inventory. Structural steel shapes are cut and mitered on a band saw to form useful brackets and supports.
Punch pressing the sheet metal forms
- 2 From the shear press, the sheet metal is loaded on a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) punch press. The punch press has the option of receiving its computer program from a drafting CAD/CAM (Computer Aided Drafting/Computer Aided Manufacturing) program or from an independently written CNC program. The CAD/CAM program will transform a drafted or modeled part on the computer into a file that can be read by the punch press, telling it where to punch holes in the sheet metal. Dies and other punching instruments are stored in the machine and mechanically brought to the punching arm, where it can be used to drive through the sheet. The NC (Numerically Controlled) press brakes bend the sheet into its final form, using a computer file to program itself. Different bending dies are used for different shapes and configurations and may be changed for each component.
- 3 Some brackets, fins, and sheet components are outsourced to other facilities or companies to produce large quantities. They are brought to the assembly plant only when needed for assembly. Many of the brackets are produced on a hydraulic or mechanical press, where brackets of different shapes and configurations can be produced from a coiled sheet and unrolled continuously into the machine. High volumes of parts can be produced because the press can often produce a complex shape with one hit.
Cleaning the parts
- 4 All parts must be completely clean and free of dirt, oil, grease, and lubricants before they are powder coated. Various cleaning methods are used to accomplish this necessary task. Large solution tanks filled with a cleaning solvent agitate and knock off the oil when parts are submersed. Spray wash systems use pressurized cleaning solutions to knock off dirt and grease. Vapor degreasing, suspending the parts above a harsh cleansing vapor, uses an acid solution and will leave the parts free of petroleum products. Most outsourced parts that arrive from a vendor have already been degreased and cleaned. For additional corrosion protection, many parts will be primed in a phosphate primer bath before entering a drying oven to prepare them for the application of the powder coating.
Powder coating
- 5 Before brackets, pans, and wrappers are assembled together, they are fed through a powder coating operation. The powder coating system sprays a paint-like dry powder onto the parts as they are fed through a booth on an overhead conveyor. This can be done by robotic sprayers that are programmed where to spray as each part feeds through the booth on the conveyor. The parts are statically charged to attract the powder to adhere to deep crevices and bends within each part. The powder-coated parts are then fed through an oven, usually with the same conveyor system, where the powder is permanently baked onto the metal. The process takes less than 10 minutes.
Bending the tubing for the condenser and evaporator
- 6 The condenser and evaporator both act as a heat exchanger in air conditioning systems and are made of copper or aluminum tubing bent around in coil form to maximize the distance through which the working fluid travels. The opposing fluid, or cooling fluid, passes around the tubes as the working fluid draws away its heat in the evaporator. This is accomplished by taking many small diameter copper tubes bent in the same shape and anchoring them with guide rods and aluminum plates. The working fluid or refrigerant flows through the copper tubes and the opposing fluid flows around them in between the aluminum plates. The tubes will often end up with hairpin bends performed by NC benders, using the same principle as the NC press brake. Each bend is identical to the next. The benders use previously straightened tubing to bend around a fixed die with a mandrel fed through the inner diameter to keep it from collapsing during the bend. The mandrel is raked back through the inside of the tube when the bend has been accomplished.
- 7 Tubing supplied to the manufacturer in a coil form goes through an uncoiler and straightener before being fed through the bender. Some tubing will be cut into desired lengths on an abrasive saw that will cut several small tubes in one stroke. The aluminum plates are punched out on a punch press and formed on a mechanical press to place divots or waves in the plate. These waves maximize the thermodynamic heat transfer between the working fluid and the opposing medium. When the copper tubes are finished in the bending cell, they are transported by automatic guided vehicle (AGV) to the assembly cell, where they are stacked on the guide rods and fed through the plates or fins.
Joining the copper tubing with the aluminum plates
- 8 A major part of the assembly is the joining of the copper tubing with the aluminum plates. This assembly becomes the evaporator and is accomplished by taking the stacked copper tubing in their hairpin configuration and mechanically fusing them to the aluminum plates. The fusing occurs by taking a bullet, or mandrel, and feeding it through the copper tubing to expand it and push it against the inner part of the hole of the plate. This provides a thrifty, yet useful bond between the tubing and plate, allowing for heat transfer.
- 9 The condenser is manufactured in a similar manner, except that the opposing medium is usually air, which cools off the copper or aluminum condenser coils without the plates. They are held by brackets which support the coiled tubing, and are connected to the evaporator with fittings or couplings. The condenser is usually just one tube that may be bent around in a number of hairpin bends. The expansion valve, a complete component, is purchased from a vendor and installed in the piping after the condenser. It allows the pressure of the working fluid to decrease and re-enter the pump.
Installing the pump
- 10 The pump is also purchased complete I h from an outside supplier. Designed to increase system pressure and circulate the working fluid, the pump is connected with fittings to the system and anchored in place by support brackets and a base. It is bolted together with the other structural members of the air conditioner and covered by the wrapper or sheet metal encasement. The encasement is either riveted or bolted together to provide adequate protection for the inner components.
Quality Control
Quality of the individual components is always checked at various stages of the manufacturing process. Outsourced parts must pass an incoming dimensional inspection from a quality assurance representative before being approved for use in the final product. Usually, each fabrication cell will have a quality control plan to verify dimensional integrity of each part. The unit will undergo a performance test when assembly is complete to assure the customer that each unit operates efficiently.
The Future
Air conditioner manufacturers face the challenge of improving efficiency and lowering costs. Because of the environmental concerns, working fluids now consist typically of ammonia or water. New research is under way to design new working fluids and better system components to keep up with rapidly expanding markets and applications. The competitiveness of the industry should remain strong, driving more innovations in manufacturing and design.
Where to Learn More
Other
"HVAC Online." 1997. http://www.hvaconline.com (July 9, 1997).
"Cold Point Manufacturing." 1997. http:/www.coldpoint.com/index3.htm (July 9, 1997).
— Jason Rude