Spray Paint
Background
Spray paint is an aerosol product designed to be dispensed as a fine mist. Compared to conventional brush methods of painting, spray painting is faster and provides a more uniform application. While industrial spray painting relies on special air compressors that break the paint particles into a fine mist, commercial spray paints are self-contained aerosol cans that use liquefied gasses to atomize the paint.
History
The art and science of painting date back more than 30,000 years. Primitive humans painted crude depictions of their lives on cave walls that are still visible today. Over the centuries, as improved methods and materials were developed, painting evolved as both a way of expressing art and as a functional tool. In 1700, the first recorded paint mill in America was built in Boston by Thomas Child. The first ready to use paints for the consumer were developed more than 150 years later by D. R. Averill in Ohio.
While these paints were commercially desired by consumers, they were also very expensive to ship around the country because of their weight. As methods of mass production became increasingly available, manufacturers learned how to make paint more efficiently. Small factories began springing up all across the country. This system of small, decentralized manufacturing plants allowed manufacturers to sell paint across the nation. This system persisted in the industry until the mid twentieth century.
In the 1940s, the paint industry took another step forward with the invention of the aerosol can. Originally developed by the military as a tool to dispense insecticide, aerosol systems were quickly adapted to other product categories including spray paint. In 1948, the Chase Company in Chicago became one of three businesses licensed by the United States Department of Agriculture to make aerosol mosquito repellents. Using similar technology and equipment, a few years later they became the first commercial producers of spray paint.
Since its birth in the 1950s, the spray paint industry has enjoyed considerable success but has also met with many challenges. In the late 1970s, legislators banned paints from using chlorofluorocarbon propellants (CFCs) due to the role these solvents are though to play in atmospheric ozone depletion. In the late 1990s, the California Air Resource Board (CARB) began imposing limits on the amount of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) that can be used in spray paint. VOCs have been shown to contribute to air pollution. These regulatory mandates have dramatically affected the quality of spray paint formulations. In spite of these challenges, spray paints continue to be popular consumer commodities. In 1997 nearly 25 million gal (94 million 1) of spray paint where produced in the United States alone.
Raw Materials
Pigments
Pigments are used in spray paint to provide color and opacity. There are four basic types of pigments used in spray paint. White pigments such as titanium dioxide are used to scatter light and make the painted surface more opaque. Color pigments, as the name implies, provide color to the paint mixture. These include a variety of synthetic chemicals. Inert pigments are used as fillers that alter the film characteristics of the paint. Finally, functional pigments provide extra performance characteristics such as imparting protection from ultraviolet rays.
Pigments must be chosen carefully because they can also affect certain formulation characteristics such as viscosity. If the pigments are not properly dispersed they may agglomerate, that is they may come together to form larger clumps that will settle to the bottom of the container. When this occurs the pigments are not able to be separated into small enough particles to spray through the valve.
Solvents
Solvents are the liquids that carry the rest of paint ingredients. While water is a good solvent for many materials, it is slow in drying and tends to cause corrosion in metal cans. Therefore, non-aqueous, quick drying solvents are used. Solvent selection can also affect the stability of the pigment dispersion. Some solvents may absorb on to the outer layer of the particle and cause it to swell—this interaction helps stabilize the dispersion. Other types of solvents, on the other hand, can have a negative effect upon the pigment dispersion. If the solvents completely cover the surface of the particle they can prevent the interaction of other ingredients and may actually destabilize the formula
Propellants
Propellants are gasses that force the paint out of the can by expanding rapidly when the valve is opened. Chlorofluorocarbon gasses (CFCs) were originally used as propellants but these were banned from use in 1978 because it was discovered that they deplete the ozone layer. Other gasses like butane and propane were used as replacements for CFCs. These hydrocarbons are classified depending on the amount of pressure they create in the can. Butane 40, for example, is a mixture of butane and propane and has a vapor pressure of 40 psi (2.8 kgf/cm 2 ) per square inch. Hydrocarbon propellants were used as primary propellants until the 1980's when the California Air Resource Board determined that these chemicals contribute to smog. They passed regulations that limited the amount that could be used in spray paint. To solve these problems, a new class of propellants known as Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) where developed for use in aerosols. These include and 1,1,-difluoroethane (Propellant 152A) and 1, 1, 1, 2,-tetrafluoromethane (Propellant 134A).
Other Ingredients
Other ingredients are included in the formula to stabilize the pigment dispersion, to control pH and viscosity and to prevent corrosion in the can.
Packaging
Spray paints are packaged in tin plated steel or aluminum cans. The can is sealed with a valve that controls how the paint is dispensed. The top of the valve is a button that controls the shape of the spray; it is attached to the valve body that acts as a mixing chamber for the liquid paint concentrate and the propellant. At the bottom of the valve a plastic tube is attached that carries the paint upward from the bottom of the can.
The Manufacturing
Process
Batching the concentrate
- 1 The first step in manufacturing aerosol spray paint is to prepare the liquid concentrate in large metal or glass tanks. This process involves mixing the liquid ingredients such as solvents, corrosion inhibitors, and pH and viscosity control agents with large impeller type mixers driven by electric motors.
Dispersing the pigments
-
2 The critical step in the manufacturing process is ensuring that solid
pigment particles are properly dispersed. Care must be taken to ensure
that the liquid displaces all the air surrounding the particles. Simple
mixing with a propeller blade is not enough to disperse the pigments, so
special mixing equipment such as a ball mill is used. A ball mill is a
circular container, like a drum, that is filled with ceramic or
stainless steel balls. The dry pigments are mixed with some of the paint
concentrate to form a slurry that is poured into this drum. The drum is
then placed on a pair of rotating metal rollers; as
it spins around, the balls tumble in the drum and break apart the pigment particles.
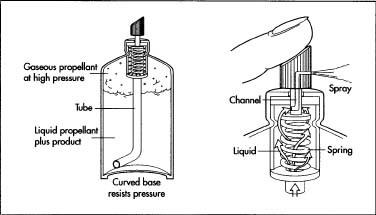 The inside of a spray paint can and how it works.
The inside of a spray paint can and how it works.Another type of mixer that can be used in this process is a roller mill that consists of two closely spaced rotating metal cylinders. The pigment slurry is passed through the rollers as they rotate against each other. The pigment particles are broken apart by the action of the rollers until only the smallest particles passed through the spacing—the larger aggregated particles are broken apart.
- 3 Once the pigments have been properly wetted, the slurry can be added to the remainder of the liquid concentrate in the batching tank. This mixture is then stirred until it is homogenous. At this point in the process a sample of the paint concentrate may be taken to check for consistency and color. If the color does not match appropriately additions can be made to the batch to adjust the color. Adjustments can be made to increase the pigment load to boost the color or to add more solvent to dilute it. Once it is known that the batch meets the appropriate specifications it can be transferred to a filling tank.
Filling process
- 4 The filling processes used for aerosols is highly automated. The empty cans travel down an conveyor belt to reach the filling equipment. Jets of compressed air blast away any dust or dirt that may be in the cans before they are filled with the concentrate by the filling heads. These heads are a series of nozzles that are connected to tubes that transfer the paint from the filling tank. A piston mechanism controls how much liquid is injected into the can. After filling the cans proceed down the assembly line to a gassing device that injects liquefied propellant into the can and then immediately crimps the valve against the rim of the can to seal it shut.
- 5 After gassing, the cans travel through a trough of hot water so they can be observed to check for leaks. If the can has a hole in it or if the valve is not sealed properly a small stream bubbles will be visible in the water bath. Faulty cans are removed and discarded. After passing through the water trough, the cans are dried with more compressed air. At the end of the assembly line an overcap is fitted over the valve to protect the aerosol from accidental activation. Finally the cans are packed into cartons and placed on pallets for shipping.
Quality Control
The quality of the spray paint product is evaluated at several stages. During batching, the concentrate is checked to ensure it is the proper shade. This may be done simply by visually comparing a sample of the fresh batch to an approved standard. A small amount of the paint can be spread on a white background to aid in this comparison. In addition, more sophisticated color-metric or photometric instrumental methods of analysis may be used. Analytical test methods, such as the Daniels Flow Point Test, are used to ensure that the paint dispersion will be stable. During the aerosol filling process random samples are pulled from the assembly line to be checked. Critical evaluations include fill weight, the solids concentration, and the pressure of the can. Spray rate (the amount of paint delivered per unit time) and spray pattern (the size and shape of the spray) are carefully evaluated as well. After manufacture is complete, accelerated aging studies may be done to ensure that the cans will spray without clogging and that the inside of the cans remain free from rust.
The Future
The aerosol spray paint industry faces a variety of future challenges involving both marketing and technical issues. As the market has matured, manufacturers struggle to find new ways to market their products. The Krylon company (a division of Sherwin-Williams) is gearing future marketing efforts in two new areas. One new product line is aimed toward woman and children with paints that offer bright new colors, enhanced washability, and a new fresh fragrance. The other line is targeted toward specific home contractor applications such door/shutter paint, vent paint, and tread and grip paint.
In addition to marketing challenges, future paint formulators will have to continue to search for ways to reduce cost or improve performance. Examples of future technology can be found in two new formulation approaches. One deals with two new solvents that improve the appearance of the paint film after drying and the other involves a reduced pigment-fill-to-binder ratio that improves surface coverage. Finally, other future challenges that aerosol spray paints face include environmental regulations meant to control VOC emissions and global warming, legal issues regarding safety labeling, and continued product abuse by graffiti artists.
Where to Learn More
Books
Johnsen, Montfort A. The Aerosol Handbook. Wayne Dorland Company, 1982.
Periodicals
Johnsen, Montfort A. "Aerosols—The VOC Challenge Moves into the 21st Century." Spray Technology 11 (1999): 21.
Other
"Economic Value of Paints and Coatings." National Paint & Coatings Association Web Page. December 2001. < http://www.paint.org/indjinfo/value.htm >.
Randy Schueller
It should read: In the late 1970s, legislators banned paints from using chlorofluorocarbon propellants (CFCs) due to the role these solvents play in atmospheric ozone depletion.
Jayesh Shah
Ruchak Enterprise
India